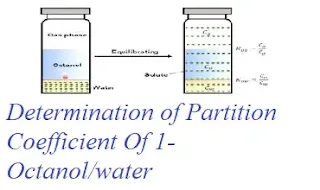
Aim: To determine 1-octanol/water partition coefficients of ofloxacin, norfloxacin, lomefloxacin, ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin and pipemidic add from 293.15k to 323.15 by shake-flask method.
Principle: If a solute/drug is added to two immisicible liquids such as oil(organic phase) and water(aqueous phase) in contact with each other, the solute/drug distributes itself between the two liquids and an equilibrium is set up between the solute molecules in oil and solute molecules in water. The ratio of the concentration of the solute in the two liquids is known as distribution coefficient or partition coefficient.
Partition coefficent of a drug is a measure of how well a substance distributes or partitions between a lipid (oil) and water. High partition coefficient means more tendancy to distribute in lipids and less partition coefficent means less tendency to distribute. Partition coefficient in the range of 1 to 2 is supposed to predict passive absorption as high lipid solubility high enough to facilitate partitioning of the drug in the lippoidal membrane into blood vessels.
Requirments:
Chemicals:
- Quinolones: Ofloxacin, norfloxacin, lomefloxacin, ciprofloxacin, pefloxacin and pipemidic acid.
- Double distilled water.
- The mixtures were then stirred in a mechanical shaker for 1h. samples were left in water bath and kept at the appropriate temperature(0.02k) for at least 72h.
- after that, the aqueous phases were isolated and the concentrations were determined by measuring the UV absorbance.
- The partition coefficents were calculated by mass balance. All the partitioning experiments were performed in at least triplicate. 1-octanol/water parttion coefficents of dprofloxicin and sulfamethazine listed in Table 1 were measured.
Table:1 Measurment values for 1-octanol/water partition coefficents (IgKow) of some substances at 298.15k
| Substance | IgKow exp | Igkow ref |
|---|---|---|
| Ciprofloxicin | 1.0825 | 1.0800 |
Kow=co/cw
Where, Kowis 1-octanol/water partition coefficent of quinolone.
co is the concentration of quinolone in 1-octanole phase at equilibrium.
cw is the concentration of quinolone in aqueous phase at equilibrium.
Kow is actually the phase equilibrium constant for quinolone partitioned in 1-octanole phase and aqueous phase saturated with each other at some temperature.
Observation and result:
| Substance | 'co' Concentra tion of quinolone in 1-octanole phase |
'cw' Concentrat ion of quinolone in aqueous phase |
Partition coefficent Kow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cipro floxicin |
Log p(K) =C1/C2
Where, K=partition co-efficent,

Post a Comment